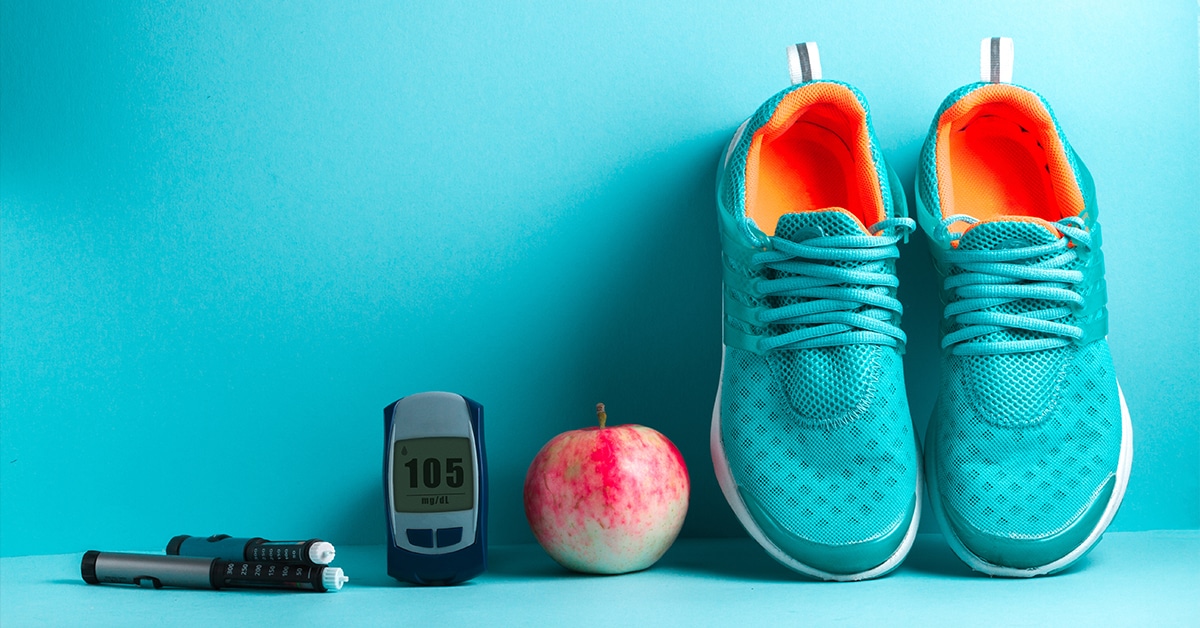
Diabetes remains one of the most prevalent chronic diseases in America, and the number of American adults diagnosed with the disease has doubled over the past two decades. As of 2018, one in 10 American adults—just over 34 million—had diabetes, according to the latest National Diabetes Statistics Report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Additionally, an estimated one in three American adults—about 88 million—have prediabetes. Of perhaps more concern, though, is that the vast majority of Americans with prediabetes don’t even know that they have it, according to the report.
The potential silver lining in these otherwise startling statistics is that diabetes can be managed, and those with prediabetes can undertake lifestyle changes to help prevent its onset into full-blown diabetes. The internal medicine focus on treating the whole patient rather than just a specific disease works perfectly with treating diabetes and prediabetes. Dr. B sees this first-hand at her Naples, Florida practice, where her holistic approach helps her patients manage blood sugar levels to keep diabetes at bay. Read on to learn more about diabetes and how you can manage the condition- or help prevent its onset- with specific lifestyle changes.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition caused when your body doesn’t make enough insulin or cannot effectively utilize the insulin it produces. Insulin is instrumental in controlling blood sugar levels as it helps regulate sugar intake at the cellular level. A lack of insulin or malfunction of cellular response to insulin elevates blood sugar levels, which can cause serious health problems over time, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney disease (leading cause of kidney failure)
- Vision loss (leading cause of adult blindness)
- Nerve Damage
- Skin problems
- Hearing impairment
- Increased risk of dementia
- Lower limb infection (that can lead to amputation)
Health impacts from diabetes develop over time, with the condition’s duration and poorly controlled blood sugar levels dictating the risk of complications. Given time, diabetes can become life-threatening and is considered the seventh leading cause of death among American adults.
Type of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is the rarest type representing between 5-10% of all diagnosed diabetes cases. This type is believed to be caused by a malfunctioning immune system response and there are no known preventive cures. Usually diagnosed during the childhood to young adult years, type 1 diabetics need daily insulin injections to survive.
The most prevalent type of diabetes is type 2, representing 90-95% of all people with diabetes. It tends to develop over time, and its two leading causes are being overweight and age (or, as Dr. B would say, those who have celebrated more birthdays). As a person ages, the pancreas secretes less insulin over time. This causes blood sugar to rise.
Symptoms, which are often slow to emerge, include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unusual hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Numbness or tingling in extremities
- Blurry vision
- Exceptionally dry skin
- Increase in infections
- Sores that are slow to heal
- Constant fatigue
Gestational diabetes can develop in some women during pregnancy as a result of hormonal changes, which causes some insulin resistance in all women late in pregnancy. Most gestational diabetics recover normal insulin function after pregnancy, but about 50% will eventually develop type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes presents when blood sugar levels are elevated, but not high enough to result in a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. These elevated blood sugar levels put prediabetics at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, but lifestyle changes can help prevent the full onset of the disease.
Preventing and Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
Whether you’ve been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, healthy lifestyle changes can be key to their control and/or prevention. According to the CDC, simple changes in diet and exercise can help reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes by as much as 58%. If you are overweight, a 5-7% drop in overall body weight is enough to make a difference. For those who’ve maintained a sedentary lifestyle, the CDC notes that 30 minutes a day, five days a week of brisk walking or similar activity can be equally effective.
These lifestyle changes are also strongly recommended as part of the management plan for controlling type 2 diabetes. Other type 2 diabetes control measures include:
- Regular blood sugar testing
- Proactive management of high or low blood sugar levels
- Insulin when needed
- Symptom monitoring to control other potential health impacts early
- Stress management
Consult with Dr. B to Learn More
Dr. B’s focus on whole health rather than a condition-specific approach, works perfectly with controlling type 2 diabetes and helping prediabetes patients keep the condition from fully taking hold. If you would like to learn more about diabetes management, have elevated blood sugar levels, or have experienced symptoms related to diabetes, you can contact Dr. B’s Naples-based internal medicine practice today through our easy online form, or by calling (239) 261-9990.